中国西南天文研究所活动星系核团组发布高度完备的z~2 AGN光谱样本
SWIFAR Releases a Spectral AGN Catalog with High Completeness at z~2
活动星系核(Active Galactic Nuclei , AGN)指位于星系中心发出强电磁辐射的超大质量黑洞及其近邻区域,正在经历剧烈的物质吸积及黑洞质量的快速增长。作为宇宙中活动最为剧烈的特殊天体,大天区完备的AGN样本对研究超大质量黑洞、星系及宇宙的演化意义非常。
HETDEX巡天是一个大规模无预选源的光谱巡天项目,旨在通过观测宇宙“正午时期”高空间完备度的天体红移,对宇宙三维空间进行精细测绘,进而研究宇宙暗能量的演化。HETDEX巡天使用位于美国德州的十米霍比-埃伯利望远镜,该望远镜具备积分视场光谱仪阵列,可以完成大规模的红移测量,单次曝光(6分钟)可同时获得34944条光谱。
新利18体育新活动星系核课题组基于与HETDEX项目组的密切合作,于近期公开发布了HETDEX巡天最新的AGN样本。该样本覆盖63平方度,AGN数密度为253.4个每平方度,是目前数密度最高的大天区光学AGN样本。以往的AGN光谱巡天往往利用图像巡天的亮度、颜色和形态筛选出光谱后随样本,HETDEX巡天因其无预选源的特色,使得传统光谱巡天中少被观测的低光度塞夫特星系、尘埃高度遮蔽的红AGN得以被认证。此外,其空间可分辨的光谱信息也有利于研究红移z~2附近的 AGN电离气体的空间延展性质,从而帮助我们研究AGN对宿主星系、星系周乃至星系际介质的电离辐射和运动学影响。
该工作已被国际天文学主流期刊《天体物理学杂志增刊系列》(ApJS,中科院1区top)接收,预印本链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19414 。新利18体育新刘辰旭副研究员是文章第一作者和唯一通讯作者,参与该研究的合作者包括 Karl Gebhardt教授(德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校), Erin Mentuch Cooper博士(麦克唐纳天文台), Dustin Davis博士(德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校), Donald P. Schneider教授(宾夕法尼亚州立大学), Matt J. Jarvis教授(牛津大学), Daniel J. Farrow博士(赫尔大学), Steven L. Finkelstein教授(德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校), Oscar A. Chavez Ortiz博士(德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校),以及HETDEX项目组。
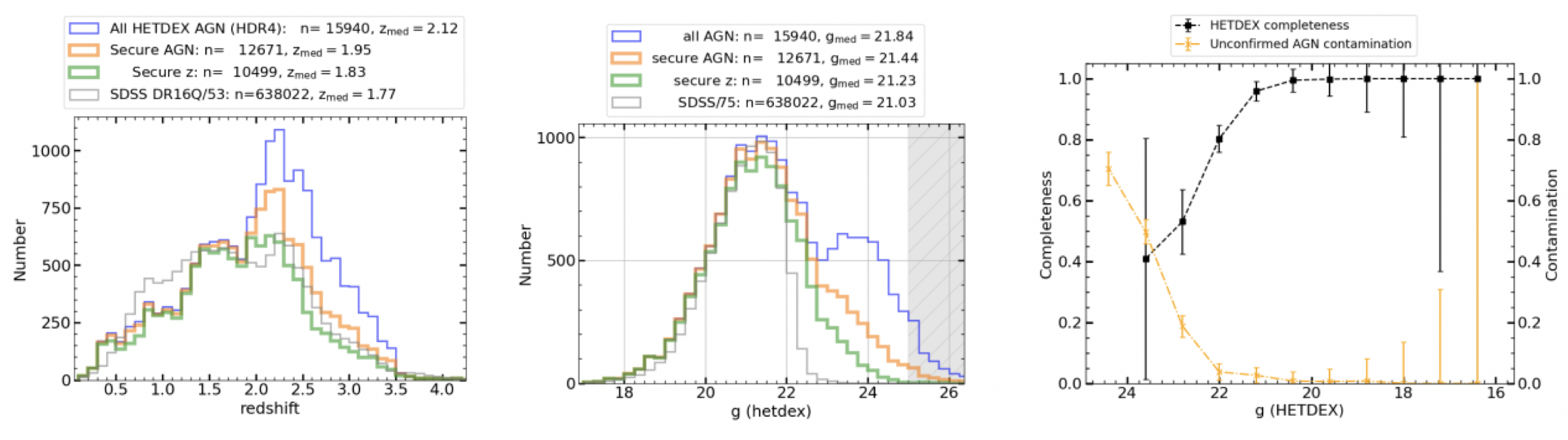
图1左和中图:HETDEX AGN的红移分布和g波段星等分布图。右图:HETDEX AGN在不同亮度区间的完备度和纯度表现。
Figure 1 Left and Center: The redshift and g-band magnitude distributions of HETDEX AGN. Right: Completeness and contamination of HETDEX AGN across g-band magnitudes.
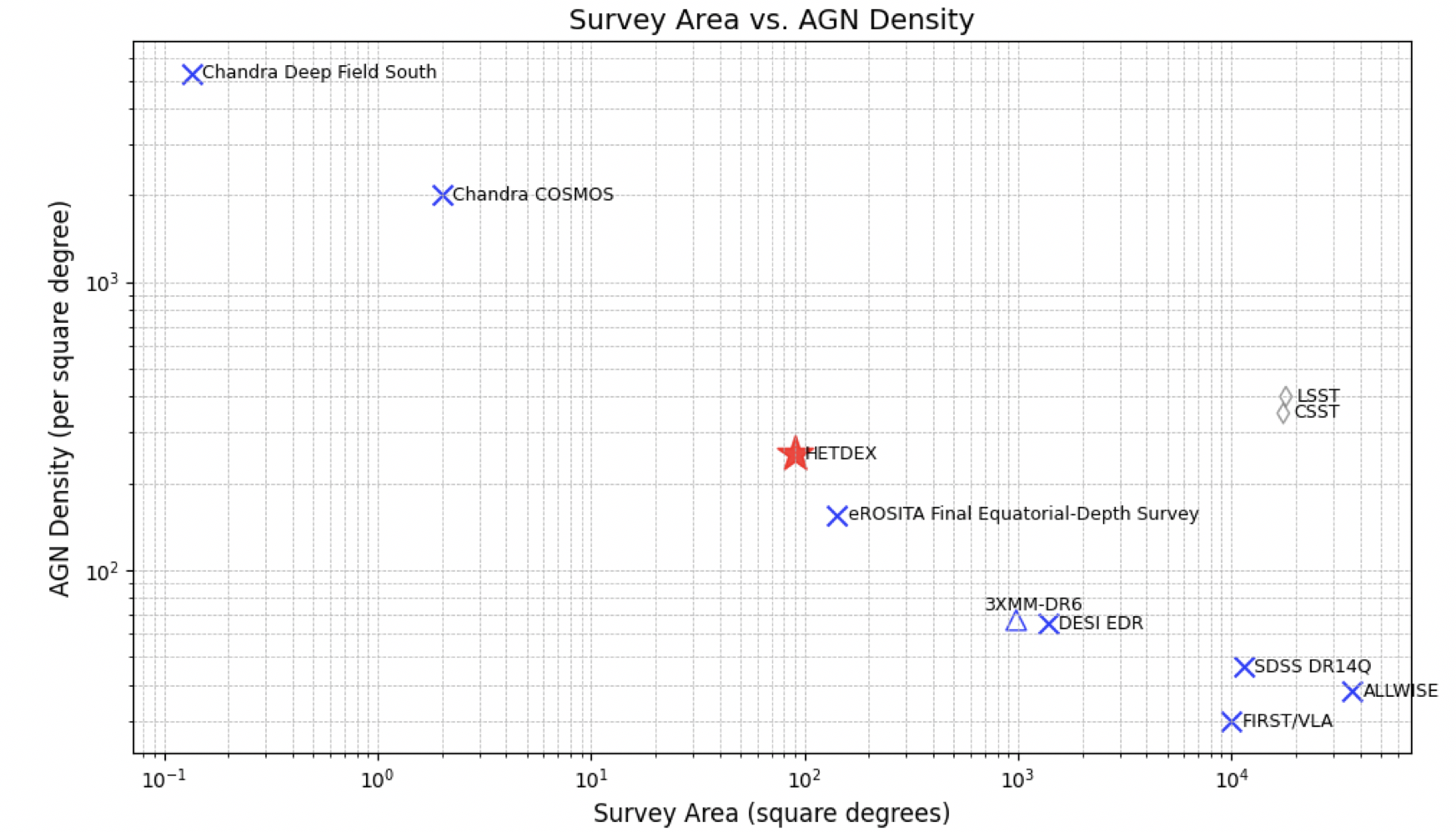
图2. 目前世界上一些大型巡天的天区覆盖面积和AGN数密度图。其中,HETDEX为本工作依托的光学光谱巡天;CSST和LSST是正在建设中的下一代巡天望远镜;Chandra、eROSITA和XMM是X射线空间望远镜。
Figure 2: Sky coverage and AGN number density of major astronomical surveys worldwide. CSST and LSST represent next-generation surveys under construction, while Chandra is an X-ray space telescope.

Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) are supermassive black holes and their surrounding areas located at the centers of galaxies that are undergoing intense matter accretion and rapid mass growth, emitting strong electromagnetic radiation. As the most active and extreme objects in the universe, AGN samples with high spatial completeness across large sky areas are crucial for studying the evolution of supermassive black holes, galaxies, and the universe.
The Hobby-Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment (HETDEX) is a large-scale, untargeted spectroscopic survey aimed at mapping the three-dimensional structure of the universe with high spatial completeness by measuring the redshifts of celestial objects during the cosmic noon epoch. Utilizing an array of integral field spectrographs (IFS) on the 10-meter Hobby-Eberly Telescope in Texas, HETDEX can perform massive redshift measurements, capturing 34,944 spectra simultaneously in a single 6-minute exposure.
Recently, the AGN research group at the South-Western Institute For Astronomy Research (SWIFAR, Yunnan University), in collaboration with the HETDEX team, publicly released the latest AGN sample from the HETDEX survey. This sample covers 63 square degrees with an AGN number density of 253.4 per square degree, making it the highest-density large-sky-area optical AGN sample to date. Traditional AGN spectroscopic surveys typically rely on photometric pre-selections based on brightness, color, and morphology. However, the untargeted nature of the HETDEX survey enables the identification of previously underrepresented AGN types, such as low-luminosity Seyferts and heavily obscured red AGNs. Furthermore, the spatially resolved spectral data allow for studies of the spatial extension of ionized gas in AGNs at redshifts around z∼2, helping to explore the ionization and kinematics impacts of AGN on their host galaxies, circumgalactic medium (CGM), and intergalactic medium (IGM).
This work has been accepted by The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series (ApJS). The pre-print is available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19414. Dr. Chenxu Liu, an associate research professor at Yunnan University, is the first and corresponding author of the paper. Collaborators include Prof. Karl Gebhardt (University of Texas at Austin), Dr. Erin Mentuch Cooper (McDonald Observatory), Dr. Dustin Davis (University of Texas at Austin), Prof. Donald P. Schneider (Pennsylvania State University), Prof. Matt J. Jarvis (University of Oxford), Dr. Daniel J. Farrow (University of Hull), Prof. Steven L. Finkelstein (University of Texas at Austin), Dr. Oscar A. Chavez Ortiz (University of Texas at Austin), and the HETDEX collaboration.
