天文学家发现M87星系中黑洞喷流周期性进动
Precessing jet nozzle connecting to a spinning black hole in M87
超大质量黑洞、吸积盘和喷流之间的能量传输机制已困扰了物理学家和天文学家一个多世纪。目前,一被广泛接受的理论认为黑洞的角动量是能量的来源,然而,超大质量黑洞的自旋尚没有直接的观测证据。
由来自全球45个研究机构的科研人员组成的国际科研团队通过分析多个甚长基线干涉测量网从2000年至2022年的观测数据,发现M87星系中心黑洞喷流呈现周期性摆动,摆动周期约为11年,振幅约为10度,见图(1)。这一现象符合广义相对论预测的旋转黑洞导致的参考系拖拖曳效应。这项研究成果成功地将M87星系中心黑洞喷流的动力学与该星系中心超大质量黑洞的状态联系起来,为M87黑洞自旋的存在提供了观测证据。这项研究于北京时间2023年9月27日发表在《自然》上。
除了有力地说明了M87的超大质量黑洞自旋的存在,这项成果还提供了关于M87中的黑洞、吸积盘和喷流系统的重要的结构信息。比如,喷流的摆动幅度较小,这意味着喷流的方向、吸积盘的角动量和黑洞的自旋轴的方向相近,另外,11年的进动周期也暗示着吸积盘相对比较小,这些结构信息对日后事件视界望远镜的数据分析和对数值模拟都有很大的帮助。
新利18体育新的副研究员林伟康深度参与了该研究,对其中的数据分析和理论解释均作出了重要贡献。
科学联系人:林伟康,新利18体育新,weikanglin@ynu.edu.cn。
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06479-6。
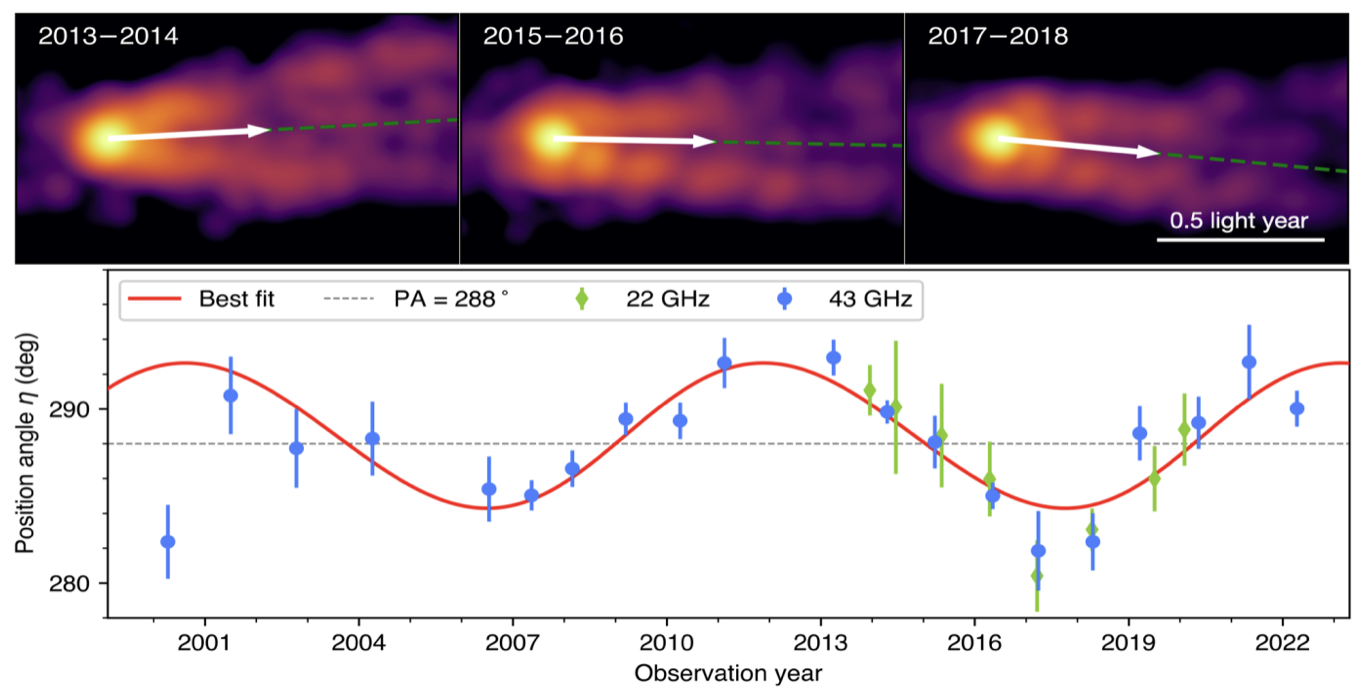
图(1):上图:2013年至2018年期间每两年合并后的M87喷流结构。下图:基于2000年至2022年数据拟合的喷流角度的变化曲线。绿色点和蓝色点分别来22GHz和43GHz的观测频段的数据。(来源:Yuzhu Cui et al. 2023)。
Figure 1. Top panel: M87 jet structure at 43 GHz after bi-yearly stacking data observed during 2013-2018. Bottom panel: Best fitting results based on the yearly-stacked image from 2000 to 2022. The green and blue points are obtained from observations at 22 GHz and 43 GHz, respectively. Credit: Yuzhu Cui et al. 2023.

图(2): 林伟康副研究员在解释黑洞的自旋所引起的吸积盘进动。
Figure 2. Associate research professor Weikang Lin explaining the accretion disk precession caused by a black hole spin.

The energy transfer mechanism among supermassive black holes, accretion disks, and relativistic jets have been puzzling physicists and astronomers for over a century. A prevailing theory suggests that energy can be extracted from a spinning black hole, allowing some materials surrounding the supermassive black hole to be ejected with great energy. However, the spin of supermassive black holes, a crucial factor in this process and the most fundamental parameter besides the black hole mass, has not been directly observed.
An international collaboration consisting of researchers from 46 institutes tackled this challenging question by closely monitoring long-term evolution of the jet in galaxy M87. The team analyzed the data obtained over the last 23 years via Very Long Baseline Interferometry and found the jet swinging up and down with an amplitude of about 10 degrees and a period of about 11 years; see figure (1). The result can be successfully explained with the precession of a tilted accretion disk predicted by the general-relativistic frame dragging effect caused by a spinning black hole. It serves as a smoking gun for the existence of M87’s black hole spin. The work is published in Nature on September 27th, 2023.
In addition, the finding provides important structural information about the M87 black hole-accretion disk-jet system. For example, the small precession angle implies a small misalignment between the jet and the M87 black hole spin. A precession period of 11 years suggests a rather compact accretion disk. Such information will be important for the analysis in the direct black hole imaging as well as the theoretical and numerical models of the black hole-accretion disk-jet system.
Weikang Lin, an associate research professor at the South-Western Institute for Astronomy Research Yunnan University, is a core collaborator of this work. Lin contributes to both the data analysis and the theoretical interpretation of the results.
Contact: Weikang Lin, South-Western Institute for Astronomy Research, Yunnan University, weikanglin@ynu.edu.cn.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06479-6.
