新利18体育新范祖辉教授与访问学者Oleg Yu Tsupko博士提出黑洞阴影作为宇宙学标准尺
Black hole shadows as standard rulers for cosmological studies
“事件视界望远镜”合作组首次成功获得了M87星系中心的大质量黑洞的“照片”,并于2019年公布(见图一),这一成果打开了探索黑洞的新窗口。展望未来观测的发展,新利18体育新范祖辉教授和研究所访问学者Oleg Yu Tsupko 博士提出了利用黑洞阴影作为“标准尺”测量宇宙学距离的方法。
根据广义相对论理论,阴影的物理半径主要取决于黑洞的质量,因此如果能够准确测量黑洞质量,则黑洞阴影可以作为“标准尺”,通过观测其角直径大小,可以得到宇宙学距离。图二显示了理论计算的不同质量的黑洞在不同红移处的阴影角半径。可以看出,如果下一代事件视界望远镜的分辨率能够达到1微角秒,则有望在红移<0.1的范围内,得到质量为10^9-10^10太阳质量黑洞的阴影图像,进而用来测量宇宙学距离。该方法独立于标准烛光测距法,有助于理解哈勃常数不一致的问题。如果分辨率可以达到0.1微角秒,对于质量大于10^9太阳质量的黑洞,则可以观测到红移1以上的黑洞阴影,从而测量高红移宇宙学距离,开展宇宙学研究。
需要指出的是,从观测上实现该测距方法,除需高分辨率黑洞阴影观测外,还需要对黑洞质量的准确测量和对黑洞吸积盘、喷流等结构的理解。虽然目前难以实现,但天文观测和理论的快速发展有望使该方法在未来成为独立的宇宙学测距手段。该研究工作已在国际专业学术期刊《经典与量子引力》(Classical and Quantum Gravity)发表(文章链接:https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6382/ab6f7d)。

图1. M87中心黑洞阴影图像。Black hole shadow of M87 (ETH Collaboration 2019, ApJL, 875, L4) .
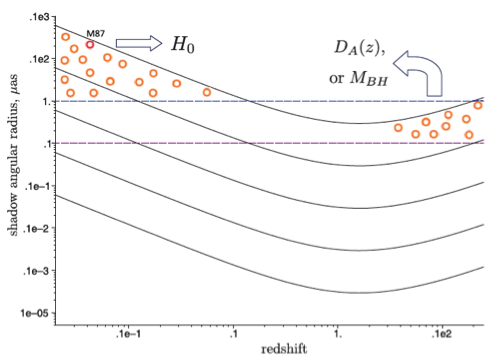
图2: 阴影角半径随红移的变化,不同线给出了黑洞质量为10^6,10^7,10^8,10^9和10^10太阳质量的结果(从下到上)。Shadow angular radius vs. redshift. Different lines, from bottom to top, are the results for black hole mass of 10^6,10^7,10^8,10^9, and 10^10 solar mass, respectively. (Tsupko, Fan, & Bisnovatyi-Kogan, 2020, Class. Quantum Grav. 37, 065016)

In 2019, Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration released the very first image of a black hole and its shadow, the supermassive black hole at the center of M87 galaxy (Figure 1). The paradigm-shifting observations have opened a new window for probing black hole physics. Foreseeing the future developments of the field, in their 2020 paper published in Classical and Quantum Gravity, Prof. Zuhui Fan of SWIFAR and the SWIFAR visiting fellow Dr. Oleg Yu Tsupko proposed to use black hole shadows as “standard rulers” for cosmological distance measurements.
According to the theory of General Relativity, the physical size of a black hole shadow is mainly determined by its mass. Therefore if we can measure the black hole mass accurately, its shadow size is known. By observing the angular extension of the shadow, we will then be able to derive the angular diameter distance to the black hole. Figure 2 shows the theoretical calculations of the angular size of shadow vs. redshift and the dependence on black hole mass. It is seen that if future advanced EHT can achieve a resolution of 1μas, for black holes with mass of 10^9 to 10^10 solar mass, their shadows can be observed in the redshift range up to z~0.1. This, in turn, will allow us to derive their cosmological distances independent of standard candles, providing useful clues to the H0 tension problem. If the resolution can further reach 0.1μas, the shadow observations can even be done for black holes with mass above 10^9 solar mass up to z~1 and beyond, and therefore make the cosmological studies possible.
It is noted that to realize the proposed method, we need not only high-resolution shadow observations, but also an accurate determination of the mass of a black hole and the thorough understanding of its accretion disk and jet structures. It is still beyond the reach of current observations. However, with the fast observational and theoretical developments, in the future our proposed method can potentially provide independent distance measurements for cosmological studies. The paper has been published in the Classical and Quantum Gravity (article link: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6382/ab6f7d).
