国际首台多通道测光巡天望远镜(梦飞)
在丽江高美古天文观测站建成,实现蓝黄红三通道同时出光
The Multi-channel Photometric Survey telescope (Mephisto), the first of this type in the world, finished construction at Gaomeigu, Lijiang, and realized the first light in blue, yellow and red channels simultaneously
2023年12月21日,作为世界上首台大视场多通道测光巡天望远镜,由中国西南天文研究所提出并主持研制的云南大学“双一流”建设重大科技基础平台——多通道测光巡天望远镜(梦飞)在云南丽江高美古建成,首次获得蓝黄红三通道同时拍摄的天体图像。12月27日中国西南天文研究所召开首光新闻发布会,得到了人民日报,新华社,中国新闻网等主流媒体广泛报道。
天文学是研究宇宙基本规律的科学,以科学为导向、观测为基础、发现为驱动,是21世纪最为活跃的前沿科学。巡天是天文学研究的起点,是发现和探索新天体、新现象,深入研究各类天体性质及其形成和演化的基础和前提。当代天文学研究已迈入多信使、全波段、大规模巡天的蓬勃发展时代。时域天文学成为天体物理学新的突破口,蕴含了巨大的发现空间,有望在探索动态演化宇宙、揭示新物理等方面取得重大突破。
国际上正在实施和即将开展的多个巡天计划每晚将探测到数以千万计的变源及暂现源候选体。如何对这些海量候选体进行实时快速证认与分类,并从中挑选出最具研究意义的源开展后续精确测量和研究,是当前时域天文学面临的主要瓶颈。获取高精度实时颜色信息是打破此瓶颈的关键,将对提高变源、暂现源证认分类的可靠性和效率发挥重要作用。精确实时的颜色还将使精确测定海量统计无偏恒星样本的物理化学性质(有效温度、表面重力加速度、金属丰度,以及年龄)成为可能,为研究恒星结构、形成和演化,揭示银河系及一般星系的结构、星族组成及集成历史提供重要基础性数据。
梦飞巡天望远镜是国际首台大视场、多通道高精度成像巡天望远镜,视场直径2度,将配备3台超大靶面、总像素高达10亿的拼接大靶面电子耦合探测器相机,可同时在3个波段【蓝通道:u(紫,345纳米)或v(蓝,389纳米)波段;黄通道:g(绿,527纳米)或r(黄,625纳米)波段;红通道:i(橙,830纳米)或z(红,937纳米)波段)】拍摄天体图像,提供天体超高精度测光及颜色信息,录制宇宙天体运动和变化的彩色纪录片。2018年1月6日,项目通过科学论证专家评审会,1月11日正式立项。望远镜主体由南京天文光学技术研究所负责研制,2018年9月通过详细设计方案专家论证会。2021年6月与云南天文台合作,完成丽江高美古台址(东经100°02′ , 北纬26°42′ , 海拔3200米)建设。2022年8月,包含覆盖望远镜全视场(直径2度)四分之一(约44角分)的蓝/黄红分色立方棱镜及改正镜系统的望远镜主体(小系统)完成出所验收。2022年9月,望远镜开始进行在站安装调试,配备2台安道尔iKon-XXL单芯片相机,并于10月23日实现蓝、红2通道初光,展现良好像质。2023年3月,第二块小系统黄/红分色立方棱镜研制成功。2023年12月,1台由国家天文台宇宙大尺度结构与巡天研究团组自主研制的单芯片相机到位,12月21日首次实现蓝黄红三通道同时出光。
望远镜现搭载的3台超大靶面单芯片相机虽仅覆盖可用视场的四分之一,但已具备很强的科学观测能力。自2022年10月初光以来,望远镜已试运行超过2000小时,获得7万余幅科学图像,原始图像总数据量约13T。调试期间,对标准星(场)以及多类变源、暂现源,包括太阳系小行星,球状星团中的天琴座RR型脉动变星,仙女座大星云(M31)及风筝星云(M33)等近邻星系中的经典造父变星,新近探测到的超新星、潮汐瓦解事件及伽马暴候选体、活动星系核等,进行了多历元多波段监测,取得重要观测数据,即将发表一批重要科学成果。近期,望远镜将启动为期一年的先导巡天。覆盖全视场的分色立方棱镜系统以及拼接大靶面电子耦合探测器相机已在研制中,预计2024年底到位。
各新闻媒体报道链接:
人民日报:https://wap.peopleapp.com/article/7298760/7136565
新华社:https://h.xinhuaxmt.com/vh512/share/11833166?d=134b43b&channel=weixin
中国新闻网:https://m.chinanews.com/wap/detail/chs/sp/10136366.shtml
光明日报:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BUTWiHrDMFqOogwaa0SWMg
丽江日报:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Nyx3LzjmpZfcETlUz7SMcw
梦飞巡天望远镜及首光图片视频介绍:
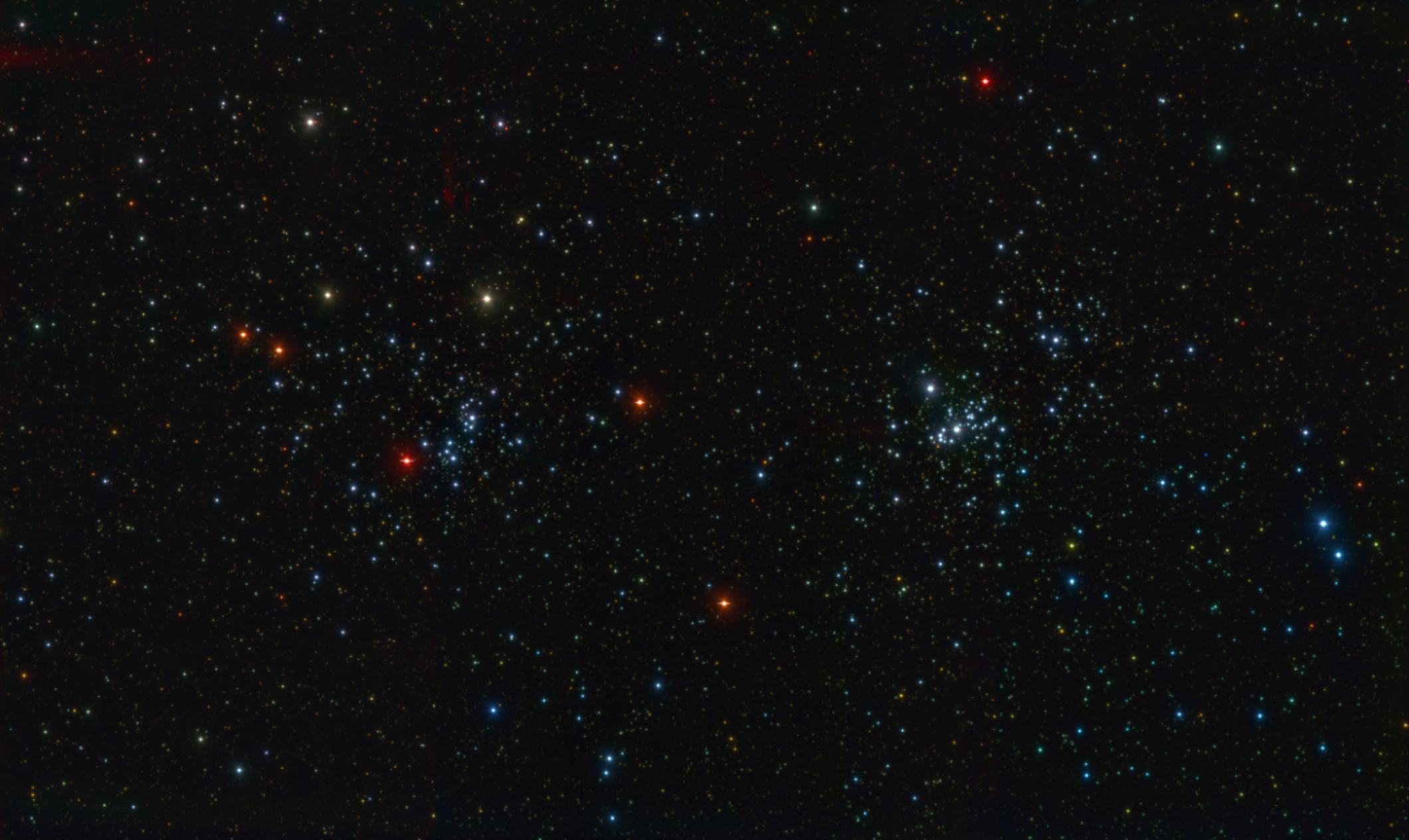

图1. 梦飞望远镜及终端相机(同时)拍摄的ugi三波段合成的NGC884 & NGC869疏散星团的首光真彩色图像。Fig. 1 The first composited true color image (ugi) of open cluster NGC884 & NGC 869 by Mephisto.

图2. 梦飞望远镜三通道成像首光新闻发布。

图3. 梦飞望远镜三通道成像首光新闻发布。

图4. 梦飞望远镜三通道成像首光新闻发布,崔向群院士致贺词。

图5. 景益鹏院士致贺词。

图6. 赵刚院士致贺词。

图7. 吴雪峰副台长致贺词。
图8. 梦飞望远镜项目负责人、中国西南天文研究所长刘晓为教授接受媒体采访。

On December 21, 2023, the Multi-Channel Photometric Survey Telescope (Mephisto), proposed and led by SWIFAR, finished construction at the Gaomeigu in Lijiang, Yunnan. It successfully captured first images simultaneously in the blue, yellow, and red channels. On December 27, the SWIFAR held the first light press conference, which was widely reported by mainstream media such as People's Daily, Xinhua News Agency, and China News Service.
Astronomy is the science that studies the fundamental laws of the universe. Driven by scientific principles, based on observations, and propelled by discoveries, it is one of the most active frontiers in the 21st century. Large-scale surveys serve as the starting point for astronomical research, providing the foundation for discovering and exploring new celestial bodies and phenomena, as well as for in-depth studies of various celestial properties, their formation, and evolution. Contemporary astronomical research has entered a vibrant era of multi-messenger, all-wavelength, and large-scale sky surveys. Time-domain astronomy become a new breakthrough, offering tremendous discovery potential in exploring the dynamic evolution of the universe and revealing new physics.
Several ongoing and upcoming international projects are expected to detect millions of variable and transient candidates per night. How to perform real-time and robust identification and classification of these candidates, and select the most important ones for follow-up observations, is the bottleneck in time-domain astronomy. The key to break this bottleneck lies in obtaining high-precision real-time colors. Accurate real-time colors will be also important to determine the physical and chemical properties (effective temperature, surface gravity, metallicity, and age) of a statistically large and unbiased stellar sample, providing fundamental data for studying stellar structure, formation and evolution, and revealing the stellar population and assembly history of the Milky Way and other galaxies.
The Mephisto is a wide-field, multi-channel, high-precision photometric survey telescope, the first of its type in the world. It has a 1.6m primary mirror, covers a field-of-view (FOV) of 2°in diameter and will equipped with 3 wide-field CCD mosaic cameras boasting a total of 1.0 Giga pixels, capable of simultaneously imaging the same patch of sky in three channels: blue (u or v band - 345 or 389 nm), yellow (g or r band - 527 or 625 nm), and red (i or z band - 830 or 937 nm). Mephisto will yield real-time colours of astronomical objects with unprecedented accuracies, and deliver for the first time a coloured documentary of our evolving universe. Following a scientific review panel on January 6, the project was officially approved on January 11, 2018. The telescope was developed by the Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics & Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). In June 2021, in cooperation with Yunnan Observatories, CAS, the site construction at the Gaomeigu (100°02′ E, 26°42′ N, altitude 3200 meters) was completed. In August 2022, the telescope with the cubic prism (blue / yellow and red) and corrector system (covering 1/4 field-of-view, small system) passed the in-house evaluation. In September 2022, the telescope, equipped with two Andor iKon-XXL single-chip cameras, began on-site installation and commissioning, and we achieved the first light in the blue and red channels on October 23. In March 2023, another cubic prism (yellow / red) was successfully developed. In December 2023, a single-chip camera independently developed by National Astronomical Observatories, CAS was installed, and we achieved the first simultaneous images in the blue, yellow, and red channels on December 21.
Although the current telescope is equipped with three single-chip cameras (covering 1/4 of the field of view), it already possesses strong observation capabilities. Since its first light in October 2022, the telescope has been in operation for over 2000 hours, capturing more than 70,000 scientific images with a total raw data volume of about 13 terabytes. During the commissioning phase, Multiple-epoch and multi-band observations were conducted on standard stars (fields), various types of variable and transients, including solar system asteroids, RR Lyrae pulsating variables in globular clusters, classical nova in nearby galaxies such as the Andromeda Galaxy (M31) and the Triangulum Galaxy (M33), as well as newly detected supernovae, tidal disruption events, gamma-ray bursts, and active galactic nuclei, resulting in important observational data and a batch of significant scientific achievements will soon be published. In the near future, we will initiate a one-year pilot survey. The large system with cubic prisms covering the entire field of view and the full-field mosaic CCD cameras are still in development and expected to be in place by the end of 2024.
